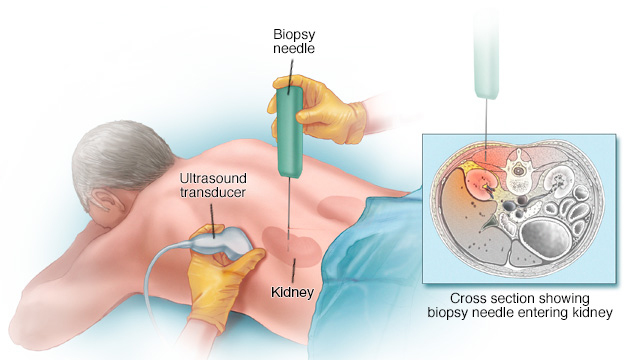
About Percutaneous Biopsy and Drainages
Percutaneous biopsy and drainages are minimally invasive procedures used to diagnose and treat various medical conditions. A percutaneous biopsy involves extracting a small sample of tissue using a needle inserted through the skin, guided by imaging techniques like ultrasound or CT scans. This procedure is commonly used to diagnose cancers, infections, and other diseases. Drainages involve inserting a catheter to remove fluids, abscesses, or cysts from the body, providing relief from symptoms and preventing complications. Both procedures offer a safer, less invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods.
Procedure
Both percutaneous biopsy and drainage procedures are typically performed under local anesthesia, often with sedation. For biopsies, a needle is inserted into the target tissue under imaging guidance to ensure precise sampling. The obtained tissue is then analyzed in a lab to diagnose the condition. In drainage procedures, a catheter is placed into the fluid-filled area using imaging techniques, allowing fluid to be removed. The procedures usually take 30 to 60 minutes, and patients can often go home the same day. Recovery is generally quick, with minimal discomfort and a low risk of complications.
Benefits
Percutaneous procedures offer several advantages, including being minimally invasive, which reduces recovery time and the risk of complications. These procedures provide accurate diagnostic information and effective treatment with minimal discomfort. They are typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home shortly afterward. The use of imaging guidance ensures precision and enhances the safety and success rates of these procedures. For patients, this means less pain, shorter recovery periods, and reduced healthcare costs compared to traditional surgical methods.
Risks
While generally safe, percutaneous biopsy and drainage procedures do carry some risks. Potential complications include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues or organs. However, these risks are minimized when the procedures are performed by experienced healthcare professionals using advanced imaging guidance. Most patients experience only mild side effects, such as temporary pain or swelling at the insertion site. It is important for patients to discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision about undergoing these procedures.
Back to Services