Introduction:
What is the thyroid gland and its functions?
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland that regulates your heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and metabolism.
What is a thyroid nodule and its symptoms?
Thyroid nodules are an abnormal overgrowth of tissue in the thyroid gland (located in your neck). These nodules can be solid or fluid-filled. Nodules on your thyroid, although common, can interfere with this gland’s proper functioning. Luckily, only about 5% of thyroid nodules end up being cancerous, but even benign (non-cancerous) ones can cause issues such as swelling at the base of the neck, a hoarse voice, coughing, difficulty breathing and swallowing, dizziness, pain and pressure, and they can become quite large and unsightly.
Nodules in the thyroid gland can affect how the thyroid functions. Nodules may or may not cause symptoms. The majority of nodules are benign and non-life-threatening, but they can still cause problems.
Some symptoms include discomfort, difficulty or pain when swallowing, production of excess thyroid hormone, as well as swelling and enlargement in the neck.
How to diagnose thyroid nodules?
Examination:
Your doctor can detect a thyroid nodule by examining your neck to feel your thyroid gland.
Ultrasound:
Thyroid ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of the thyroid gland within the neck. It is commonly used to evaluate lumps or nodules. Your doctor may also use ultrasound as a guide when performing a fine-needle aspiration biopsy.
Thyroid function tests:
Your doctor may take a blood sample to measure levels of T3 and T4—the thyroid hormones—and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH is a hormone made by the pituitary gland to regulate the thyroid’s production of T3 and T4. These blood tests cannot detect if a thyroid nodule is cancerous but will help rule out other thyroid conditions.
Fine needle aspiration cytology:
Using ultrasound to guide needle placement, your doctor takes several samples of the nodule. The samples are sent to pathology for microscopic evaluation.
Traditionally, the only treatments available for problematic thyroid nodules were thyroid surgery or radioactive iodine therapy. Today, patients who want an alternative to surgery or radiation have another option.
While thyroid surgery is an invasive surgery that requires hospitalization, general anesthesia, a lifetime of medication, and causes more pain and a longer recovery time. Additional risks specific to thyroid surgery include bleeding, scarring, hypothyroidism, damage to the vocal cord nerve, and calcium deficiency. Thyroid surgery also results in a visible scar on the neck. After surgery or radioactive iodine treatment, lifetime thyroid hormone medication is often required. You will need to have regular blood tests as your doctor determines the proper thyroid hormone dosage for you, and it may take some time before you feel your best.

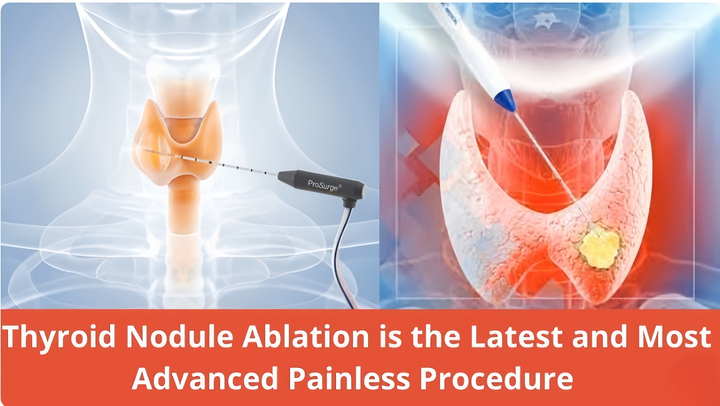
What is thyroid nodule ablation?
Thyroid nodule ablation is a painless, minimally invasive medical procedure that treats thyroid nodules. Using ultrasound-guided imaging, the nodule is located, allowing the treatment to focus solely on the targeted nodule area. Using a radiofrequency generator, your doctor allows a carefully controlled amount of energy to flow through the electrode into the tissue to ablate the nodule. With the sustained ablation thermal heat, the nodule is degenerated, allowing the degenerated tissue to flow through your body naturally as waste over the course of a few months.
Benefits of thyroid nodule ablation:
Thyroid nodule ablation is a minimally invasive option used to treat benign thyroid nodules. It is a quick, non-surgical procedure that allows most patients to resume their normal day-to-day activities immediately following treatment.
Preserves your healthy thyroid tissue, helping the thyroid to function normally without the need for lifetime medication.
A thin needle is used to avoid any surgical scars. No general anesthesia is required, which means no downtime or hospitalization.
A major clinical study showed that non-functioning benign nodules shrunk 73% in the first 6 months and up to 93% within 4 years.
Tens of thousands of patients across the globe have chosen thyroid nodule ablation to successfully treat their thyroid disease.
Surgery vs ablation:
How Thyroid Nodule Ablation Works:
To begin the procedure, a numbing medicine will be applied under the skin and around the thyroid gland. Once you’re relaxed, and your neck is numb, a thin electrode is inserted and directed into the nodule. Heat energy emitted from the electrode causes very precise destruction of the targeted tissue. The electrode is systematically guided through the entire nodule and the process is repeated until the nodule is completely treated.
Using ultrasound, your doctor will locate the nodule and insert a thin electrode into the affected area. This method ensures that the treatment is focused solely on the targeted nodule area.
Using a RF/microwave generator, your doctor will allow energy to flow through the electrode into the nodule. The radiofrequency ablates the nodule and the heat is sustained for a safe, pre-determined length of time, usually just a few minutes.
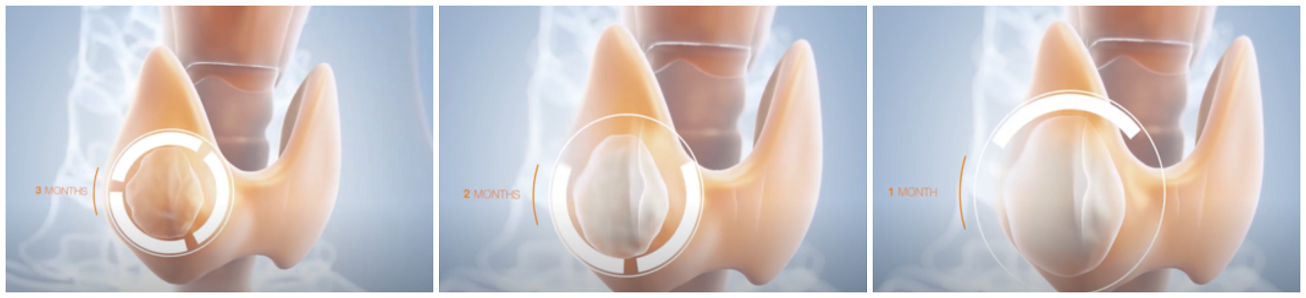
With the sustained thermal heat, the nodule is degenerated and flows through the body as waste. Most patients notice a reduction in nodule size in just 2-3 weeks.
Thyroid Nodule Ablation Procedure Experience:
Preparing for Thyroid Nodule Ablation: Your doctor will review any current medications you are taking and provide further instructions, if needed. Other than blood thinners, which you will likely need to stop taking a few days prior to the procedure, most medications do not interfere with the procedure.What to Expect During Thyroid Nodule Ablation:
You will be able to breathe, swallow, and speak normally during the entire procedure. You will be asked to lie your head on a small cushion, with your neck extended.
Your doctor will clean and prepare the skin and administer local anesthesia in the area surrounding your thyroid. To ensure that you are handling the procedure well, your doctor will ask you how you are doing and whether or not you can feel any pain. They can easily make adjustments if you are uncomfortable at any time.
When the procedure is complete, a small bandage will be placed on the treatment site and your neck may be cooled with ice packs.
What to Expect After the Procedure:
You will be monitored for a short period of time, and then discharged. You will have to check with your doctor before you drive, as you may need someone to drive you to and from the procedure. You will be able to return to most of your day-to-day activities almost immediately.
What Happens to the Nodules After the Procedure?
After the procedure, the cells of the treated thyroid nodule are removed by the body's immune system. Most patients notice a reduction in nodule size in just 2 to 3 weeks, with solid nodules taking longer than cystic nodules.The amount of reduction depends on the original size and nature of the nodules. The average is 40% to 60% reduction after three months, and about 60% to 90% reduction after one year. Years after the procedure, only the scar tissues will remain in the treated area. The nodule around the scar may still remain, but this area will be minimized after the procedure. The surrounding healthy thyroid gland will be preserved and will continue to produce thyroid hormone.
Symptoms like difficulty swallowing, pressure or tightness in the throat, or a bulky appearance of the nodule are typically eliminated or significantly reduced.
Is the Procedure Painful?
Because local anesthesia is administered before the procedure, very few patients experience any pain at all. During the thyroid ablation, it’s normal to feel pushing and pressure in the neck, but the procedure generally does not cause pain. Patients occasionally feel heat or discomfort in the neck that may radiate to the ear or jaws.Following your procedure, you will be given ice packs and pain medication, if needed. For more questions related to the procedure, please consult directly with your doctor.
How Many Treatments Are Necessary?
One procedure will sufficiently decrease the size of the nodules and improve symptoms, but if the treated nodules are close to vocal cord nerves or nodules are very large, additional procedures may be necessary to significantly decrease the nodule. The untreated areas of nodules may impede the improvement of thyroid function, so complete ablation may be required and more than one procedure may be needed.
How Effective Is the Procedure?
For benign nodules, clinical trials have shown an average ablation of benign cold nodules showed volume reductions of 32.7-58.2% at 1 month and 50.7-84.8% at 6 months, while reducing symptoms and cosmetic problems.In a long-term follow-up study, nodule ablation was effective over a four-year period, with nodules consistently decreasing by 93.5%.